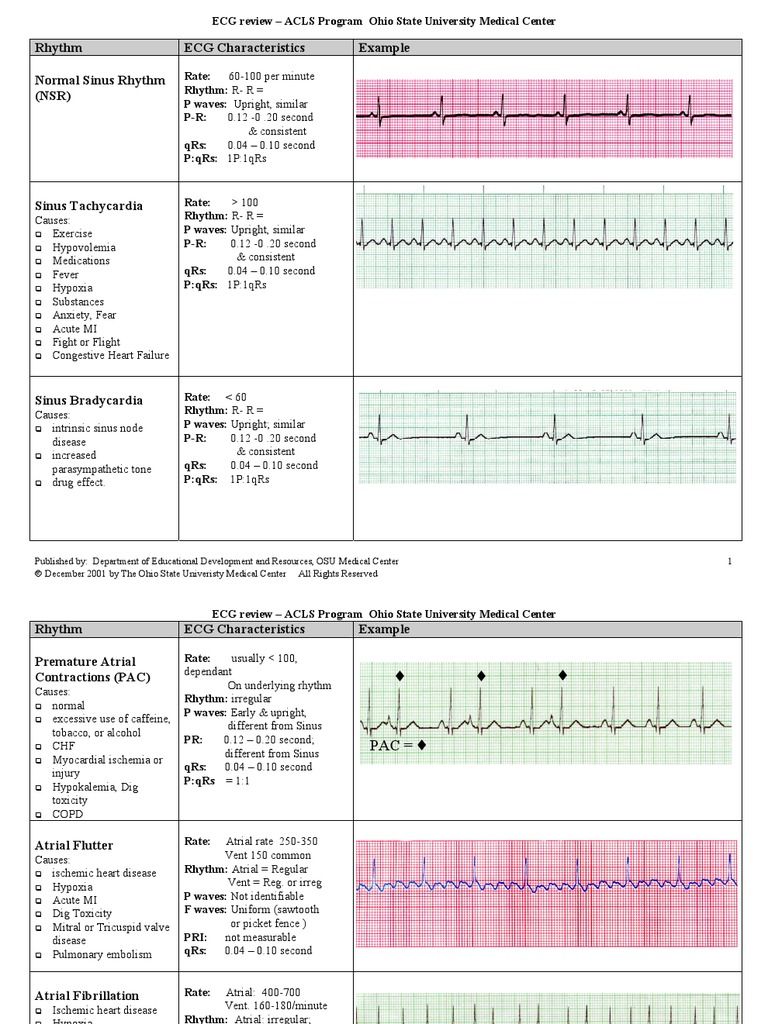
There are many clues you can learn when obtaining the ekg that will help you analyze and act on what you see. Use the squares on the ekg results to measure your heartbeat 1.

EKG Basics Nursing students, Student and Easy peasy
10 mm is equal to 1mv in voltage.

How to read an ekg strip. These squares are found on the background, behind the rhythm. Read the ekg strip 1. The qrs complex, normally starts with a downward.
Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents 0.04 seconds. Many people's ekg may vary slightly from this baseline, though, while still being completely healthy. How do you know when you need to act immediately or can wait for expert consultation?
Before you read the ekg, look for: Hr = # of boxes between r’s = 19 spaces = 79bpm 2. How to read an ecg strip.
Each larger square is 5 mm in length and represents 0.2 seconds. Here are seven tips to help you gain confidence in interpreting what you see. This can be done through the use of a caliper.
Summary of how to read an ekg. How to measure an ekg strip? Voltage is measured along the vertical axis.
How to read an ekg strip. Heart rate is 300 divided by the number of large squares, and that’s it!. Voltage is measured along the vertical axis.
Ecg paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Each larger square is 5 mm in length and represents 0.2 seconds. If you work in the medical or legal field, you’ve probably already seen an ekg strip and you know what it looks like.
The p wave indicates atrial contraction. Hint if you are suspicious that there is some atrioventricular block (av block), map out the atrial rate and the ventricular rhythm separately (i.e. By looking at the waveforms on the ekg graph you look for the p wave followed by the qrs wave and t wave in that specific order.
Mark the p waves and r waves). These signal components are called p, q, r, s, t and u. An electrocardiogram is a painless medical procedure that takes a measurement of your heartbeat that your doctor can use to analyze your heart’s health.
On the ekg, locate a r wave that matches a thick line, count the number of large squares to the next r wave. Ecg paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Here are some simple steps on how to measure the pr interval:
How do you read an ekg strip? P wave is the first short upward movement of the ecg tracing. As many values change with age;
The diagram below illustrates the configuration of ekg graph paper and where to measure the. To briefly summarize the components of a normal ekg strip, it consist of components which indicate electrical events during one heart beat. There are 5 small boxes in a large box (0.04 x 5 = 0.20 seconds).
The black marks at the top of the paper indicate 3 second intervals as seen above. Each larger square is 5 mm in length and represents 0.2 seconds. It indicates that the atria are contracting, pumping blood into the ventricles.
How to read an ecg strip. Put a marker in the paper where the “r’s” are and then measure each “r’s” in the strip. Ekg tracing please refer to the ekg tracing below if you are not familiar with the labeling of the ekg waveforms.
Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents 0.04 seconds. How to read an ekg strip ekg paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. How to read an abnormal ekg.
10 mm is equal to 1mv in voltage. Voltage is measured along the vertical axis. Locate the qrs (the big spike) complex that is closest to a dark vertical line.
To read an ekg, start by finding the voltage, which are the electrical signals of the heart and are measured along the vertical axis. Ekg paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. 10 mm is equal to 1mv in voltage.
How to read an ekg strip. If there is 1 large square between r waves, the heart rate is 300 bpm; The horizontal axis shows time and the vertical axis records ekg amplitude or voltage of the impulse.
To do it, put a piece of paper over the strip but make sure the “r” in the qrs complex is visible. Qrs = measure from start of q to end of s = 0.08 The p wave is the first component and is a short upward movement on the rhythm strip.
How many seconds is an ekg strip? Interpreting ekg rhythm strips practice strip 1. 7 steps to reading an ekg/ecg.
Before you can understand how to count the heart rate using the 6 second rule, you must first be familiar with the squares found on the ekg paper. You will need to look at the whole strip to check for an irregular heartbeat. Have your doctor administer an ekg.
Then count either forward or Full standard is two large squares (1 mv, 10 mm) and half standard is one large square (0.5mv, 5 mm) paper speed: Voltage is measured along the vertical axis.
These waveforms are labeled p, q, r, s, t and u. Each small box is 0.04 seconds and each large box is 0.20 seconds. Identify if the strip is giving a regular or irregular rhythm.
Ekg paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. How to read an ekg strip. Each small square is one millimeter and is equivalent to 0.04 seconds.
One large square is five millimeters, equivalent to 0.2 seconds. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents 0.04 seconds. An electrocardiogram will produce an ekg strip, which measures the electrical activity of your heart.
Look for consistent time intervals between spikes, which may indicate regular heart rhythm. In respect to this, what is an ekg strip? P waves = p wave for every qrs?
Pr interval = measure from beginning of p to beginning of qrs = 0.16 5. The ekg tracings are recorded on grid paper. Each larger square is 5 mm in length and represents 0.2 seconds.
These squares can be hard to see at time, so if you don’t have the best vision, you may need a small magnifying glass. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents 0.04 seconds. Each larger square is 5 mm in length and represents 0.2 seconds.
A normal ekg recording consist of components which mark electrical events in the heart. Additionally, identify the squares that measure time along the horizontal axis. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents 0.04 seconds.
The graph is broken up into two types of squares, small and large. Two large squares, 150 bpm, three large squares, 100 bpm, four… 75 bpm. Understand that the squares that are bold are designated in measurements of one second, and that they are made up of 25 squares.
The standard is 25 mm/sec, the faster the paper speed the slower the hr will look and vice versa;

Pin by Jason Winter (ECG Educator). on ECG/EKG Rhythm

12 Lead EKG Pocket Card APRN World 9781941004067 http

EKGs Made Easy How to Start Reading Rhythm Strips

Interpret EKGs Strips Like a Boss! (ekg interpretation for

96b893413bbf1593ca403123b3f6606f.jpg (736×566) Acls

Pin by Michelle Flores on Nursing in 2020 Ekg

I See All Leads / EKG Emergency nursing, Nurse, Nursing

How to Read EKG Strips Made Easy for Nursing School

Pin by Jason Winter (ECG Educator). on ECG/EKG Rhythm

EKG Reading Tips Beats per minute via box counting on the

EKG Strips test your knowledge Nursing Pinterest

Interpret EKGs Strips Like a Boss! (ekg interpretation for

ECG Interpretation Basics, Animation. Ecg interpretation

EKG cheat sheet Nurse, Ekg interpretation, Cardiac nursing

Normal and abnormal ECG Ekg, Abnormal, Ecg interpretation

Pin by Saving American Hearts, Inc. on Saving American

EKG Interpretation Nurse teaching, Ekg, Nursing mnemonics

EKG strips! Nursing stuff! Pinterest
EKG Examples Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File



